In this article, you will learn what is Neuron? it’s structure & Types.
Contents:
1. What is Neuron?
2. Structure of Neuron
3. Types of Neuron
1. What is Neuron?
Neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are specialized to perform to produce signals. These signals can be communicated over short or long distances. They can be sent from one part of an animal’s body to another. Neurons have two important properties.
(I) Excitability, the ability to respond to stimuli &
(II) Conductivity, the ability to conduct signals.
2. Structure of Neuron
Neuron contain three principal parts: a cell body, dendrites and an axon.
1. Cell body: The cell body has a large central nucleus.
2. Dendrites: The extensions of the cell body which conduct signals toward the cell body are called dendrites. The motor neuron has many short, thread like dendrites.
3. Axon: The process that conduct signals away from the cell body is called axon. The axon is a relatively long and cylindrical.
4. Myelin Sheath: The laminated lipid Sheath around the neuron is called myelin. It covers the axon of the neuron. Sometimes, it also covers dendrites. The neurons of Hydra and Sea anemones don’t have a myelin sheath. Other invertebrates and all vertebrates have sheathed neurons.
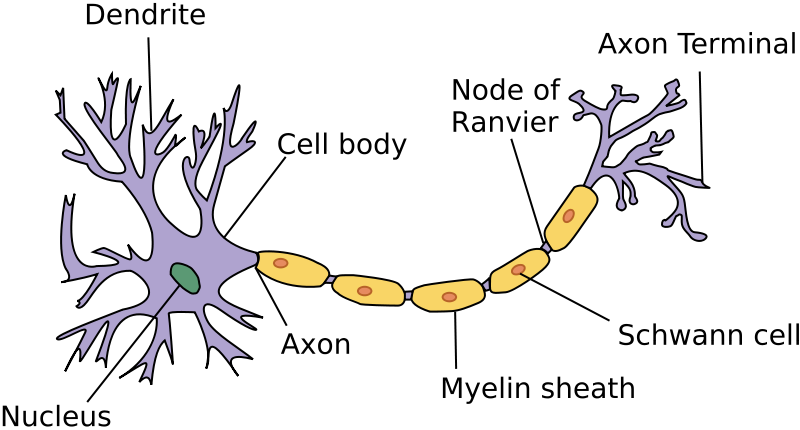
4. Schwann cell: are present in some neurons. They wrap the myelin sheath in layers. Some gaps are left in these neurons. These gaps are called neurofibril nodes or nodes of Ranvier. These nodes make the myelin sheath segmented at regular intervals. These cells are also help in the regeneration of injured myelinated neurons.
3. Types of Neurons
There are three functional types of neurons. These are sensory, inter and motor nuerons.
(I) Sensory Neurons
The neurons which transmits nerve impulse from receptor to central nervous system is called sensory neuron.
(II) Interneurons
The neurons which form the integrading center are called Interneurons. They receive signals from the sensory neurons and transmits them to motor neurons.
(III) Motor nuerons
The neurons which transmits the nerve impulse to effectors are called motor nuerons. The effectors show response. Effectors may be muscles or glands. Muscles show response by contraction. Glands show response by secretions.